Abdominal pain after eating can be a distressing experience for many individuals. It can range from mild discomfort to severe, sharp pains, making it difficult to enjoy meals or function normally throughout the day. Severe abdominal pain after eating is a common symptom, often related to various underlying issues such as indigestion, food intolerances, or more severe gastrointestinal conditions. Dr. Ksheetij Kothari, one of the best gastroenterologist in Pune, emphasizes that paying attention to the timing and nature of the pain is crucial in determining its cause and treating it effectively.
Dr. Kothari specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, with particular expertise in peptic ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and gallstones. His clinical experience has established him as a leading stomach specialist in Pune for patients experiencing abdominal pain and related symptoms.
Is it Normal to Have Abdominal Pain After Eating?

Occasional abdominal discomfort after eating is common and often linked to mild digestive issues like indigestion, gas buildup, or overeating. However, if the pain becomes severe, persistent, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as bloating, nausea, or changes in bowel movements, it may indicate an underlying condition that requires attention.
Conditions like acid reflux (GERD), food intolerances, or even gastrointestinal disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) can cause more serious or frequent abdominal pain after meals. It’s essential to distinguish between normal post-meal discomfort and symptoms that may indicate a health concern.
What are the Possible Causes of Abdominal Pain After Eating?
Severe stomach pain after eating can be attributed to a range of conditions, from mild to more serious concerns. The following are some common causes of abdominal pain:
- Abdominal Bloating After Eating:
Excess gas buildup or digestive issues can lead to bloating and pain, especially after meals.
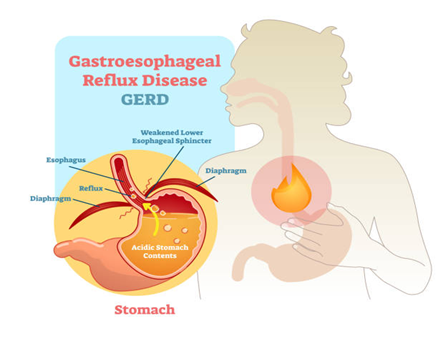
- Gastric Reflux (GERD):
This occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and a burning sensation after eating.
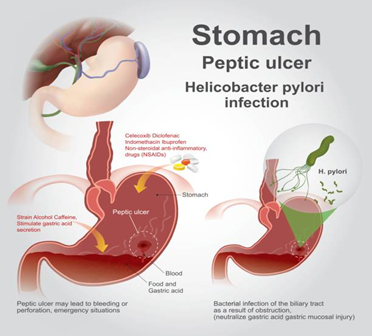
- Peptic Ulcers:
These are sores that develop on the stomach lining, often causing sharp pain after meals, particularly when the stomach is empty or after eating spicy foods.
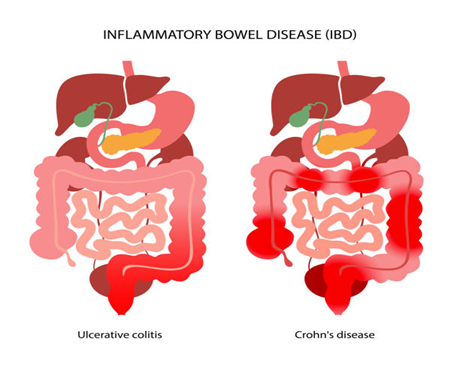
IBS can cause bloating, cramping, and severe abdominal pain after eating, especially if trigger foods are consumed.
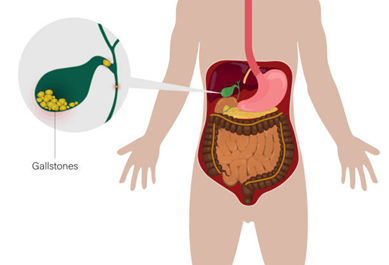
- Gallstones Abdominal Pain:
Gallstones can obstruct bile flow, causing intense abdominal pain after eating fatty or greasy foods.
- Food Intolerances or Allergies:
Certain foods, such as dairy, gluten, or high-FODMAP foods, can trigger abdominal discomfort in individuals with intolerances.
What Are the Treatments for Severe Abdominal Pain After Eating?
Treatments for stomach pain after food intake vary based on the cause of the discomfort. Dr. Ksheetij Kothari, an experienced gastroenterologist in Pune, prescribes a range of treatments tailored to the individual needs of each patient.
- Medicine for GERD:
For gastric reflux leading to discomfort, medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers can treat stomach acid and alleviate symptoms.
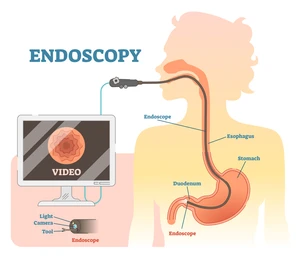
- Endoscopic Peptic Ulcer Treatment:
For ulcers of bacterial infection, endoscopy can be used to visualize the ulcer and, in some cases, cure the ulcer immediately. On top of that, antibiotics and acid-reducing drugs are prescribed to heal the ulcer.

- Dietary Changes for IBS:
For irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) pain, dietary changes—such as following a low FODMAP diet or avoiding specific triggers—can help reduce bloating, cramping, and post-meal stomach pain.
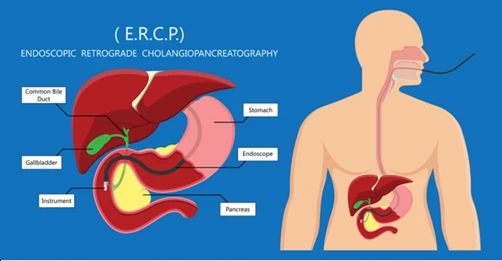
- Endoscopic Procedures for Gallbladder Problems:
When gallstones are causing pain, endoscopic methods such as Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) may be employed to remove bile duct obstructions or identify associated problems, thereby providing relief from discomfort.
- Probiotics for Bowel Imbalance:
When there is an imbalance of gut flora, probiotics can be consumed to restore a normal balance of bacteria, facilitating digestion and alleviating bloating and abdominal pain.
- Pain Management:
Over-the-counter medications, such as antacids or acetaminophen, can help manage mild to moderate pain; however, they should be used only for short-term relief.
Your treatment plan will be based on the severity of your symptoms and the cause of your pain.
When to Worry About Sharp Abdominal Pain?
Get immediate medical care if you have:
* Sudden severe pain: May be a sign of a serious condition such as gallstones or appendicitis.
* Pain with fever: May be indicative of infection or inflammation.
* Blood in stools or vomit: Indication of a severe gastrointestinal problem.
* Unintentional weight loss: May be associated with a chronic illness such as cancer.
* Pain following consumption of fatty foods: Could be suggestive of gallstones or a gallbladder problem.
* Chronic pain: If pain does not alleviate or increases, get medical attention right away.
Dr. Ksheetij Kothari, one of the best gastroenterologist in Pune, advises that if you are experiencing such symptoms, don’t delay seeking professional care.
Conclusion
Severe stomach pain after meals should never be overlooked, particularly if it has been a constant complaint. Whatever the cause – a benign condition such as indigestion or something more complex, like gallstones or peptic ulcers after meals – knowing the cause is essential for successful treatment. Visiting a gastroenterologist, such as Dr. Ksheetij Kothari, guarantees you receive the best possible care, specially suited to your particular symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can relieve discomfort and enhance the quality of your life.
FAQs
What foods should I avoid if I experience stomach pain after eating?
What causes severe abdominal pain after eating?
How can I relieve abdominal pain after eating?
When should I seek medical attention for abdominal pain after eating?
Can stress cause stomach pain after eating?
Are there any natural remedies for abdominal pain after eating?
How can I manage gallstone-related pain after eating?
Reference links:
https://www.healthline.com/health/stomachache-after-eating
https://www.verywellhealth.com/postprandial-p2-1945064
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes and not for promotional use.

